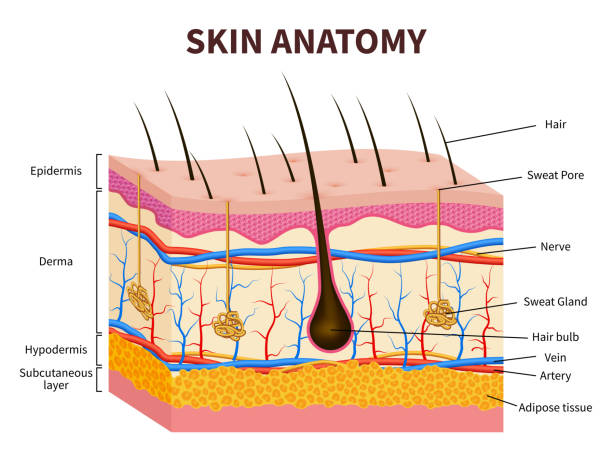
2. Layers of the Skin:
1. Introduction to Skin Anatomy:
- Epidermis: Describe the outermost layer consisting of epithelial tissue.
- Dermis: Explain the middle layer composed of connective tissue.
- Hypodermis: Discuss the deepest layer containing fat and connective tissue.
3. Epidermis:
- Structure: Detail the layers of the epidermis, including the stratum corneum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, and stratum basale.
- Functions: Explain the role of the epidermis in waterproofing and providing a barrier against pathogens.
4. Dermis:
- Structure: Discuss the composition of the dermis, which includes collagen, elastin fibers, blood vessels, nerves, and appendages such as hair follicles and sweat glands.
- Functions: Highlight the dermis’s role in providing strength, elasticity, and sensation to the skin.
5. Hypodermis:
- Structure: Describe the hypodermis as a layer of adipose tissue and connective tissue.
- Functions: Explain its role in insulation, cushioning, and storing energy.
6. Blood Supply to the Skin:
- Vasculature: Discuss the network of blood vessels that supply nutrients and oxygen to the skin.
- Importance: Explain how adequate blood supply is crucial for skin health and wound healing.
7. Nerve Supply to the Skin:
- Sensory Nerves: Describe the sensory nerves responsible for touch, temperature, and pain perception in the skin.
- Motor Nerves: Explain how motor nerves control functions such as sweating and piloerection.
8. Appendages of the Skin:
- Hair Follicles: Discuss the structure and function of hair follicles in regulating body temperature and providing sensory input.
- Sweat Glands: Explain the role of sweat glands in thermoregulation and excretion.
- Sebaceous Glands: Describe sebaceous glands and their function in lubricating the skin and hair.
9. Aging and the Skin:
